Bitcoin-based BRC-20 tokens have been making headlines in recent days. Cryptocurrency enthusiasts, especially Bitcoin maximalists, are eagerly exploring this new technology, driven by the possibility of groundbreaking BRC-20 token projects. The rapid rise of Pepe (PEPE) meme coin has raised numerous questions about the BRC-20 token standard. Let’s take a closer look at this new trend to address the lingering questions.
What are BRC-20 Tokens?
BRC-20 tokens are an experimental token standard that uses ordinal inscriptions and JSON data to deploy token contracts, mint tokens, and facilitate token transfers on the Bitcoin network. Unlike Ethereum’s EVM-based token standards that rely on smart contracts to manage token standards and rules, BRC-20 tokens are a way to store a script file on Bitcoin. This script file is used to assign tokens to satoshis (the smallest unit of Bitcoin) and enable their movement between users.
The popularity of the BRC-20 standard can be attributed to its ease of use and flexibility. Its foundation on Bitcoin, the most widely used and secure network, has attracted more investors and developers towards BRC-20. Unlike ERC-20 tokens based on smart contracts, BRC-20 tokens do not utilize smart contracts for token transactions. Instead, they leverage ordinals and inscriptions. Additionally, BRC-20 tokens require a Bitcoin wallet for minting and trading, making them more accessible to Bitcoin users.
The Emergence of the BRC-20 Standard
The BRC-20 token standard was created on March 8, 2023, by a Twitter user named @domodata. @domodata conducted an experiment via their Twitter account to see if Ordinal theory would facilitate interchangeability on Bitcoin.
Throughout the experiment, @domodata shared the progress from the conceptual stage to the BRC-20 token transfer. You can access the BRC-20 experiment notes by clicking here.
How to Create BRC-20 Tokens?
Creating tokens on Bitcoin using the BRC-20 standard is not overly complex or cumbersome. Anyone who follows the application guidelines and examines BRC-20 resources can create and utilize their own token. The process of creating BRC-20 tokens is as follows:
- Deploy a Token Contract:
- Create a JSON file that defines the details of your token contract, including a four-letter name, maximum supply, decimal places, and a mintage limit. For example, you can name your token “MYTK,” set the maximum supply to 1,000,000 tokens, decimal places to 8, and the mintage limit to 0 (if you don’t want to allow further minting).
- Use a wallet that supports ordinal numbers and inscriptions to write the JSON file to a satoshi. This process will distribute the initial set of tokens and assign them to your wallet address.
- Mint More Tokens:
- If you want to mint additional tokens for your BRC-20 token, create a new JSON file with the necessary details. This file will be shorter since you don’t need to specify all the information from the initial distribution.
- Use the same wallet that supports ordinal numbers and inscriptions to write the new JSON file to another satoshi. This will generate more tokens for your BRC-20 token.
- Token Transfer:
- To transfer tokens from your BRC-20 token to another wallet address, specify the number of tokens you want to transfer, the name of the token contract you distributed in the first step (e.g., “MYTK”), and the recipient’s address.
- Inscribe the JSON file onto a satoshi using the same wallet. This will decrease the token balance in your wallet address and increase the balance in the recipient’s wallet address.
It is important to be aware that BRC-20 tokens are still in the experimental phase and have potential risks and vulnerabilities. Scammers have already exploited vulnerabilities such as double spending on certain BRC-20 wallets. Be careful when dealing with BRC-20 tokens and use trusted wallets and platforms.

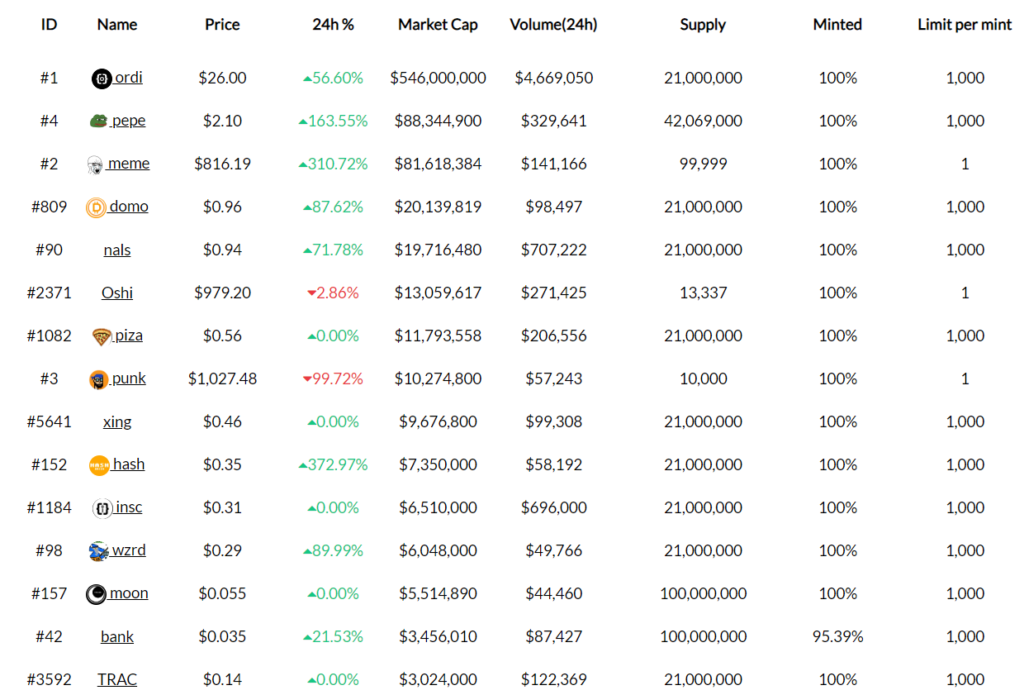
BRC-20 Token List
The overall market value of BRC-20 tokens continues to grow at an explosive rate. According to brc-20.io data, there are 14079 BRC-20 tokens as of May 8, 2023. The growth of these tokens is such that the number of BRC-20 transactions is greater than the number of Bitcoin (BTC) transactions.
BRC-20 Tokens vs. ERC-20 Tokens
Although the BRC-20 and ERC-20 are confused for various reasons, such as the origin of the BRC-20 tokens being inspired by the ERC-20, there are important differences between the two standards.
Functionality: BRC-20 tokens are not smart contracts and therefore lack the ability to interact directly with other protocols or applications on the Bitcoin network. In contrast, ERC-20 tokens on the Ethereum network have the flexibility to interact with a wide variety of decentralized applications (dApps) by enabling features such as lending, borrowing, and more.
Storage: BRC-20 tokens use ordinals and writes to store data in satoshis on the Bitcoin blockchain. This can be seen as a workaround, as BRC-20 tokens are not natively supported by the Bitcoin protocol. In contrast, ERC-20 tokens are an integral part of the Ethereum protocol; which makes their storage and processing more seamless and supported.
Availability: BRC-20 tokens are still experimental and face the challenges often associated with the Bitcoin network. Transaction fees on the Bitcoin network are relatively high and scalability can be an issue compared to the Ethereum network. Bitcoin blocks are confirmed approximately every 10 minutes; this means that more than one transfer function can be registered in the same block, requiring a confirmation sequence to determine validity.
Overall, while BRC-20 tokens offer a way to create and transact on the Bitcoin blockchain, they currently have less functionality, face storage challenges, and come with limitations associated with the Bitcoin network compared to ERC-20 tokens on the Ethereum network.
You can follow us on Twitter, Instagram, YouTube and LinkedIn to stay up to date with the latest. You can send us your questions and comments on the Telegram channel.


